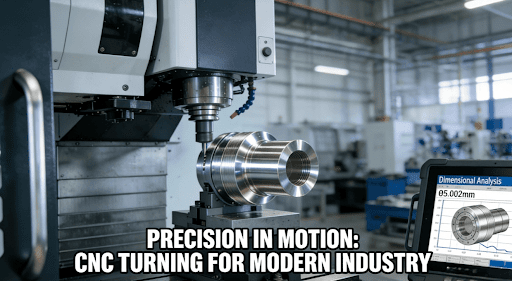
Introduction
The manufacturing tolerances have already reached their limits in miniature and complex components in industries like consumer electronics pursuing thinner, lighter, and smaller products. Defects at the micron level are enough for batch failures, leading to gigantic material waste, rework costs, and delivery delays. With quality system functions deeply embedded in manufacturing concepts, the main root causes reflect isolated processing steps and unstable process controls.
They will demonstrate that it is all about elevating precision CNC turning into a systematic engineering approach: equipment, processes, quality control, and automation integration are the keys to breaking the yield curse and achieving technological innovation.
Explain why the miniaturization trend makes consumer electronics manufacturing depend more than ever on “zero-defect” turning.
The unabated march towards smaller-size, higher-performance Consumer Electronics has made “zero-defect” manufacturing a baseline expectation, and precision CNC turning has been integral to realizing this objective. The degree of this dependence is unprecedented deepening as witnessed by the extreme miniaturization and functional integration present in state-of-the-art devices.
Market Drivers Pushing Tolerances to the Extreme
Analyses by McKinsey among others on manufacturing complexity, confirm that shorter product cycles, apart from higher component density, are pushing Tolerance requirements pushed to the extreme. In such a context, one single miniature component failure can render an entire device useless. Common CNC turned parts such as sensor housings, connector pins, and hinge shafts are exemplary of this challenge. The structural complexity is high relative to their size; their perfect interfacing with other components has to be ensured.
The High Cost of Failure
A minute deviation in some critical feature of CNC turned parts may result in any form of assembly failure or field malfunction. The cost of the resulting impact extends well beyond the part itself, entailing warranty claims, recalls, and brand damage. Thus, the attainment of a high first-pass yield is a direct determinant of profitability and supply chain competitiveness.
Process Stability Over Speed
As the International Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME) pointed out, in high-complexity manufacturing, process stability far outweighs peak speed. For Consumer Electronics, this means that a precision CNC turning process that can guarantee micrometer-level consistency across thousands of parts is indispensable. This does provide reliability for aggressive iteration cycles as demanded by the market. In other words, for systematic solutions for complex shaft parts, professional precision CNC turning services are substantially required.
H3: Yield as Core Competency
“Zero-defect” precision CNC turning helps to constantly deliver perfect CNC turned parts in an extremely competitive, margin-sensitive industry. High yield means minimal amounts of waste and smooth, seamless assembly; it is the core component of market competitiveness.
Beyond the Machine Tool: What are the essential technical elements to ensure ultra-high precision in the CNC turning process?
Relying solely on high-performance machine tools, it is far from enough to achieve and maintain a yield above 99.5%. It is a systematic project in which the synergy of multiple key technical elements needs to be conducted.
A stable CNC turning process starts by correctly compensating for machine tool thermal deformation. High-level CNC turning centers employ closed-loop cooling systems and thermal error compensation technology to make real-time counteraction of minute deformations of the spindle and guide rails caused by temperature changes. This ensures a consistent accuracy over long machining. The second aspect is the selection and optimization of high-performance cutting tools. Different geometries and coatings shall be applied to different materials to balance tool life, cutting efficiency, and surface quality.
Especially worthy of notice is the difficult-to-machine material machining process, such as precision CNC turning titanium. While titanium alloys possess such desirable properties as high strength and light weight, their low thermal conductivity and high chemical reactivity tend to promote high temperatures and work hardening during machining. Some successful machining strategies include lower cutting speeds, high-pressure coolant precise jetting, and multi-stage machining to relieve stress.
The Precision Machining Association (PMA) says that online measurement and real-time feedback systems are the heart of Advanced Manufacturing. Introduce statistical tools, such as process capability index (Cpk), in order to manage quantitatively the stability of machining so that the production process can get into a controlled state and have the data support so as to get ultra-high yields.
How does system certification, such as IATF 16949, really enable batch consistency for precision turned parts?
For any reputed precision turned parts manufacturer, certifications such as IATF 16949 and AS9100D are not badges but operational frameworks that inculcate proactive quality control into the whole precision CNC turning process, ensuring unmatched consistency from prototype to mass production.
Figure 2: The integrated quality assurance framework, driven by certifications like IATF 16949, ensures batch-to-batch consistency from raw material to final shipment.
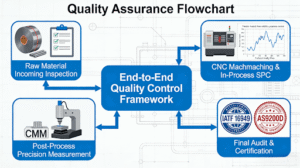
The Proactive Quality Framework
These standards transition quality assurance from a final inspection activity to a preventive process-oriented system. They put forth a structured framework that makes certain every step, from design review to production, is controlled and optimized for consistency in manufacturing precision-turned parts.
H3: Implementing Consistency through APQP & SPC
The true value of these certifications is realized through the application of mandated methodologies such as Advanced Product Quality Planning, APQP, and Statistical Process Control, SPC.
APQP for Front-Loaded Quality
APQP ensures that potential issues related to the CNC turned parts are identified and mitigated in advance during planning. This includes Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and development of a control plan before starting production, which avoids problems instead of detecting them.
SPC for real-time process control
SPC enables the monitoring of important machining parameters in real time during production. By evaluating the data trends, a manufacturer of precision turned parts can make pre-emptive adjustments for tool wear to ensure that parts remain within specification after millions of cycles. This is what constitutes end-to-end control and forms the basis of Reliable CNC turning services.
The Foundation for Trusted Tech Innovation
This is the rigorous, certification-driven system that enables Tech Innovation. It gives designers the confidence to know a perfect prototype will be identical to the millionth production part. This means they can push boundaries, knowing that their manufacturing partner will deliver reliable consistency. Adhering to such standards is a direct reflection of a manufacturer’s capability.
How has the integration of industrial automation and CNC machining cells reshaped production efficiency and reliability?
Deep integration of Industrial Automation with CNC machining cells marks the critical step towards eliminating human error for stable, high-volume production.Precision CNC turning cells, integrated with robotic loading/unloading, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), enable 24/7 unmanned “lights-out” production. In this process, manual clamping inconsistencies, operator fatigue, and other human errors are completely eliminated, redefining the repeatability accuracy of the machining process to a whole new level. For mass production of CNC turning parts, automation ensures stable production cycle times and extremely high equipment utilization rates.
More importantly, the automation systems can provide full-process data collection and traceability. For every CNC precision turning, the machining time, equipment parameters, and operator information are recorded in real time. In case of quality problems, by backtracking quickly on specific production batches and the status of the machines at that time, the efficiency of problem diagnosis and resolution would be greatly improved. High controllability and reliability mean more stable delivery commitments and a lower total cost for the customer.
Where will AI and DT drive the Future of Precision Turning Technology?
We are at the threshold of revolutionizing manufacturing technology with AI and Digital Twin technologies, as these will push the manufacturing of precision CNC turned parts to a completely new level.
By analyzing a great volume of historical machining data, AI algorithms support predictive maintenance and self-optimization of process parameters. For example, the system can make predictive warnings of tool wear status, automatically adjusting the cutting parameters to compensate for this in order to avoid batch deviations caused by excessive wear. Digital twins, by faithfully mapping an exact virtual model of the whole turning process in cyberspace, allow engineers to simulate, try out, and optimize process plans in advance of physical production, with dramatic reductions in trial-and-error cycles and improved first-time success.
This data-driven model of Tech Innovation will turn precision manufacturing from an experience-dependent “art” into a science-based “discipline.” The competitiveness of the next generation of precision CNC turned parts will largely depend on a company’s ability to use big data to make wise choices, further consolidating the advantages of high yield and low cost.
Conclusion
In the manufacturing of high-end products, the leap from 89% to 99.5% is due to deeply integrating the precision CNC turning technology, internationally standardized quality management system, and intelligent industrial automation. That’s not just a change in technique, but it represents a very fundamental shift of philosophy in manufacturing toward prevention, systematization, and information.
If the yield and stability of high-precision and complex metal parts are problematic for any given company, it is necessary to conduct a careful assessment of the systematic control capabilities and depth of a manufacturing process. It is better to initiate a technical feasibility discussion starting with specific needs.
Author Bio
Contributed by the precision manufacturing experts of JS Precision, the company specializes in customized machining solutions for high-complexity, high-precision metal parts with extensive project experience in industries like consumer electronics, automotive, and aerospace.
FAQs
Q1: What are the main metrics to assess the precision manufacturing capability of a CNC supplier?
A: More than the brand of their equipment, attention should be placed on their Cpk reports for process capability, accuracy and calibration records of their measuring equipment (e.g., CMMs), and their successful case history with difficult-to-machine materials like titanium alloys.
Q2: What are the major changes that have to be made in the turning process from prototype development through to mass production?
A: It is in the process solidification and validation-the movement from flexible fixtures to dedicated tooling, optimization of the cutting parameters to achieve the best balance between tool life and cycle time, and establishing a comprehensive SPC system.
Q3: What is usually the biggest obstacle to integrating automation?
A: Mostly, this is the standardization of data and unification of interfaces. The challenge to true interoperability is ensuring that CNC machine tools, robots, and MES systems can communicate in common protocols, such as MTConnect, for the purpose of real-time data exchange.
Q4: By what means are the main technical difficulties in precision turning of titanium alloys overcome?
A: The core is controlling heat and wear. This will involve the use of special coated tools with sharp geometries, lower cutting speeds, high pressure coolant precise jetting, and multi-stage machining to relieve material stress.
Q5: What is the real effect of international quality system certifications – such as AS9100D – on actual production?
A: They require the implementation of traceability mechanisms, tight supplier control, risk management in all aspects, such as FMEA, and a spirit of continuous improvement, ensuring control and verifiability for each part in the whole material-to-finished-product lifecycle.