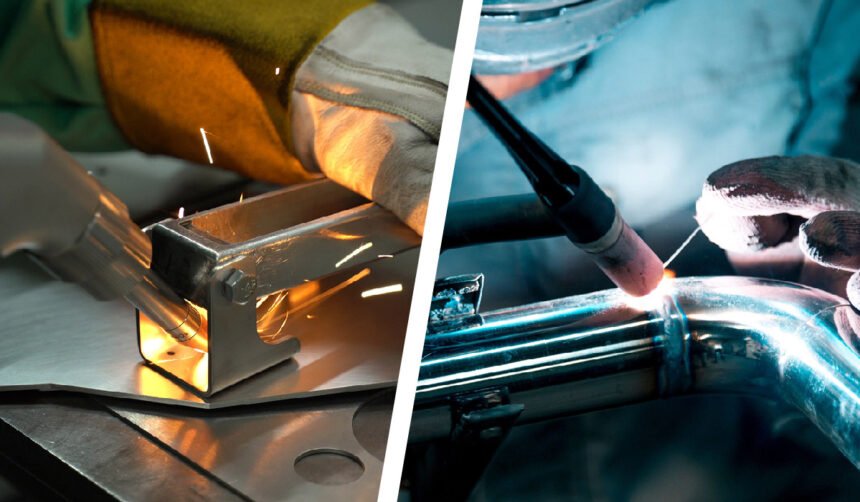
When it comes to precision welding, two of the most discussed methods are Laser Welding vs TIG Welding. Both have their strengths, and each is utilized in industries where clean, sturdy welds are critical.
But which one is better? The answer depends on your needs—speed, price, fabric type, and weld quality.
Let’s break them down and see how they truly compare.
What is TIG Welding?
TIG welding stands for Tungsten Inert Gas welding. It’s additionally referred to as GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding). This approach makes use of a non-consumable tungsten electrode and a filler rod. A shielding gas—usually argon—protects the weld from contamination.
TIG is well-loved for its high precision and clean finish. It’s frequently utilized in industries like aerospace, automobile, and custom metal fabrication. You’ll see it whilst high aesthetic quality and control are key.
However, TIG isn’t recognized for speed. It’s a slower system, and it requires a skilled hand. Welders need to hold a regular touch to control both the filler rod and the arc. That may be time-consuming, in particular with thicker substances.
What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding makes use of a concentrated laser beam to melt and join metal components. It’s a high-speed technique with pinpoint accuracy. And in contrast to TIG, it doesn’t continually require filler cloth. The beam on my own is powerful enough to penetrate even thick metals in a few programs.
This makes laser welding best for mass production and automatic systems. It’s fast, repeatable, and notably accurate. Common industries that use this technique encompass electronics, medical devices, and high-end automobile manufacturing.
The disadvantage? Laser systems are expensive to buy and maintain. The setup is more complicated, and protection precautions are stricter due to the beam’s intensity.
Key Differences Between Laser and TIG Welding
1. Precision and Finish
Both offer smooth welds; however, laser welding is even more precise. It can be targeted at tiny regions, making it perfect for sensitive components like circuit boards or micro-machinery.
TIG welding, at the same time as precise, requires a human touch and filler rod. The final result is smooth; however, it is no longer as slender or focused as a laser.
2. Speed
Laser welding is significantly quicker. In automated production, it can weld in milliseconds.
TIG is slower and hard work-intensive. That’s why it’s better suited to custom jobs or short manufacturing runs.
3. Material Thickness
Laser welding works properly with thin to medium-thickness substances. It can penetrate deep, but thick substances from time to time require a couple of passes or filler.
TIG handles thicker metals better, mainly if a robust filler weld is wanted. It’s a preferred choice for heavy-duty structural tasks.
4. Cost
Let’s speak about money. TIG welding machines are more affordable. They’re simpler and extensively available.
Laser systems? Not a lot. The high-quality laser welding machines used in enterprises can be numerous, particularly when you factor in cooling systems, protection equipment, and maintenance.
However, for high-volume production, the investment in a laser can pay off through speed and lower labor expenses.
Which Is More User-Friendly?
If you are getting to know how to weld, TIG might be a better place to begin. Yes, it requires skill; however, at least the equipment is on the market. And you get complete control over the weld pool, arc, and filler.
Laser welding is highly automatic. You won’t “feel” the process the same way. Instead, it’s about programming, calibration, and system control. Once set up, it doesn’t require consistent adjustment like TIG does.
That’s good for consistency; however, it’s not as hands-on.
When Should You Use TIG Welding?
- When running with thicker substances
- If you need maximum control and finesse
- For one-off initiatives or custom metalwork
- When aesthetics matter (e.g., visible welds on stainless steel)
When Should You Use Laser Welding?
- If you need extremely fast, repeatable welds
- For thin metals or tiny elements
- In automatic production lines
- When minimizing heat distortion is crucial
What the Experts Say
Many manufacturers use both methods depending on the task. TIG offers flexibility and is excellent for tricky welds that need a manual touch. Laser shines in high-speed manufacturing.
Even in the “Laser Welding vs TIG Welding” debate, it is no longer about which is universally better—it is about what suits the assignment at hand.
For example:
- Automotive giants use lasers to assemble car body panels quickly.
- Custom motorbike developers still lean on TIG for artistic welds on metallic frames.
- Electronics producers rely on lasers for bonding tiny wires and circuits.
Conclusion: Which One Wins?
So, is Laser Welding better than TIG Welding?
The actual answer is: it depends on your needs.
If you need speed, automation, and micro-level precision, a laser is the way to go. Especially with high-quality laser welding machines, you could reach levels of productivity that manual welding can’t match.
But if you value control, affordability, and hands-on method—in particular for thicker metals—TIG remains a gold standard.
Both are effective. Both are beneficial. It’s no longer a battle, it’s a toolbox—and understanding which tool to select will save time, money, and headaches ultimately.
You May Read Also: troozer com: Powerful All-in-One Platform That Simplifies Your Digital Life
For More Information Visit Dotmagazine