Table of Contents
The Shifting Sands of Solicitor Qualification
A New Dawn: Understanding the SQE and Its Predecessor, the QLTS
The Core Challenge: What the SQE Demands of Candidates
SQE Stage One: The Foundation of Functioning Legal Knowledge
SQE Stage Two: Mastering Practical Legal Skills
A Specialist Approach: Why Dedicated Prep is Non-Negotiable
The Seamless Transition from QLTS to SQE Methodology
Tailoring Your Journey: The Essential Components of Effective Prep
Customised Learning Plans for Varied Backgrounds
The Power of Comprehensive Study Materials
Simulating the Test: Importance of Mock Exams and Question Banks
Mastering the Skills: Deep Dive into FLK and Practical Application
Breaking Down the Functioning Legal Knowledge (FLK)
Honing the Essential Legal Skills (Practical)
The QLTS School Legacy: Building Confidence for the Modern Era
Securing Your Future: From Candidate to Qualified Solicitor
The Shifting Sands of Solicitor Qualification
The pathway to becoming a solicitor in England and Wales has undergone its most profound transformation in decades. For years, the Qualified Lawyers Transfer Scheme (QLTS) served as the robust, non-academic route for international lawyers and barristers seeking to convert their existing qualifications. It was a rigorous assessment designed to ensure foreign professionals met the exacting standards of practice required by the Solicitors Regulation Authority (SRA).
Now, the legal education landscape has been fundamentally reshaped by the introduction of the Solicitors Qualifying Examination (SQE). This new, centralised assessment is designed to be the single, mandatory route to qualification for all aspiring solicitors, domestic and international alike, replacing the old Legal Practice Course (LPC) and, crucially, superseding the QLTS.
A New Dawn: Understanding the SQE and Its Predecessor, the QLTS
The shift is significant, but the core objective remains the same: proving competence in both substantive legal knowledge and practical application. Many international candidates who were familiar with the structure and demands of the QLTS now find themselves navigating the new terrain of the SQE. Preparing for this assessment demands a strategic, specialized approach that recognizes the common competencies tested by both assessments. This is why focused, high-quality preparatory courses, such as those historically offered by QLTS School, have proven so vital—they bridge the gap between academic knowledge and the specific requirements of a standardized, high-stakes professional exam. The experience and methodology perfected under the QLTS framework are now critical blueprints for navigating the SQE.
The Core Challenge: What the SQE Demands of Candidates
The Solicitors Qualifying Examination is designed to be a holistic assessment of a candidate’s competence, split into two distinct stages that must be passed sequentially. This structure requires not only an encyclopaedic knowledge of the law but also the ability to apply that knowledge in realistic, client-facing scenarios.
SQE Stage One: The Foundation of Functioning Legal Knowledge
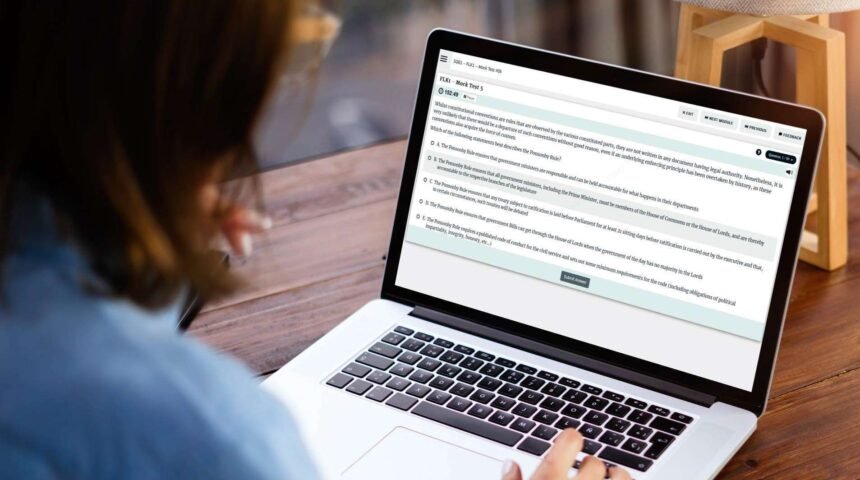
SQE1 is a closed-book, computer-based assessment comprising two examinations, known as Functioning Legal Knowledge (FLK) assessments. It tests candidates’ ability to recall and apply black letter law across a vast and comprehensive curriculum. This stage covers everything from criminal law and tort to constitutional law, property law, and professional conduct. The exams utilize single-best-answer multiple-choice questions (MCQs) that are designed to test application, not just rote memorization. Candidates must demonstrate they can function as a competent trainee solicitor, accurately identifying the relevant law and its correct application to a given factual scenario.
SQE Stage Two: Mastering Practical Legal Skills
SQE2 is the practical skills assessment. It requires candidates to demonstrate the core competencies needed to function as an entry-level solicitor, encompassing both legal research and writing skills, and crucially, client interview and advocacy skills. This stage is performed in a variety of settings (written and oral) and measures the candidate’s ability to perform tasks like conducting a client interview, drafting a contract clause, preparing a case analysis, and performing practical legal research, all under simulated real-world conditions. Passing SQE2 confirms that the candidate can, in effect, step into a solicitor’s role with the necessary practical skills.
A Specialist Approach: Why Dedicated Prep is Non-Negotiable
The breadth of the SQE curriculum, covering material typically spread across several years of academic and professional courses, makes dedicated preparation an absolute necessity. Attempting to pass based solely on prior academic qualifications, particularly if those qualifications are years old or international, is a significant risk.
The Seamless Transition from QLTS to SQE Methodology
For those familiar with the QLTS, the structure of the SQE is recognizable. The QLTS Multiple Choice Test (MCT) heavily influenced the structure and rigor of SQE1 (FLK), emphasizing the application of legal knowledge. Similarly, the QLTS Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE), which tested practical skills through simulated client interactions, is the clear predecessor of the practical skills tested in SQE2.
A preparation provider with a history of successfully navigating the QLTS exams is uniquely positioned to address the SQE. They understand the examiner’s mentality, the specific skills being tested, and how to structure a course that efficiently covers the entire body of required knowledge in a manner that maximizes retention and application under exam conditions. This specialized focus ensures candidates are not just learning the law but learning how to pass the assessment.
Tailoring Your Journey: The Essential Components of Effective Prep
Given the diverse professional and academic backgrounds of aspiring solicitors—from non-law graduates to seasoned international practitioners—an effective preparation course cannot be a one-size-fits-all solution. It must be adaptable, comprehensive, and focused intensely on the unique demands of the SRA’s assessment criteria.
Customised Learning Plans for Varied Backgrounds
The ideal prep course offers structured, flexible learning paths. For instance, a candidate with an LPC might need to focus heavily on the additional Functioning Legal Knowledge (FLK) topics not covered in their original course, while an experienced international lawyer might need to spend more time adapting their practical skills to the specific English procedural rules required by SQE2. Effective preparation utilizes initial diagnostic tests to create a schedule that addresses individual weaknesses without wasting time on areas where the candidate is already proficient.
The Power of Comprehensive Study Materials
The sheer volume of material required for SQE1 necessitates study materials that are concise, clear, and constantly updated to reflect changes in the law and the SRA’s assessment specifications. This includes:
- Core Textbooks/Manuals:Concise summaries of the required law, stripped of unnecessary academic detail, focusing on the rules of application.
- Video Lectures:Accessible explanations of complex topics delivered by experienced tutors.
- Flashcards and Summaries:Essential tools for high-volume knowledge retention and review.
The quality of the material determines the efficiency of the study process.
Simulating the Test: Importance of Mock Exams and Question Banks
The SQE is a test of endurance and technique as much as it is a test of knowledge. High-quality preparation must include:
- Extensive Question Banks:Thousands of practice MCQs written in the exact style and difficulty level of the SRA exams, crucial for mastering the single-best-answer format of FLK.
- Full Mock Examinations:Timed simulations of both SQE1 and SQE2. For SQE1, this builds the stamina needed to sit the full-day exams. For SQE2, this provides critical feedback on the specific practical and ethical marking criteria. No amount of pure study can substitute for the rigorous experience of sitting a simulated exam.
Mastering the Skills: Deep Dive into FLK and Practical Application
Success in the SQE demands that candidates move beyond theoretical understanding to confident application under pressure.
Breaking Down the Functioning Legal Knowledge (FLK)
FLK requires candidates to develop an internal filter that immediately isolates the governing legal principle from a complex factual scenario. The focus is often on procedural points, ethics, and the solicitor’s professional obligations, which permeate every area of the law tested. Prep courses must structure their learning to integrate the SRA Code of Conduct and Ethics into every legal topic, as professional standards are frequently tested across the board. The ability to identify the most correct legal outcome amongst several plausible distractors is the mark of a well-prepared candidate.
Honing the Essential Legal Skills (Practical)
SQE2 is perhaps the most challenging stage because it tests skills that often atrophy during years of academic study or that differ significantly across international jurisdictions. The key practical skills that must be honed include:
- Legal Writing and Drafting:Preparing client letters, advice memos, and contract clauses that are clear, concise, accurate, and ethically sound.
- Client Interviewing:Mastering the structure of an interview, from setting the agenda to effective questioning, listening, and providing preliminary advice in a professional manner.
- Legal Research:The ability to efficiently navigate and utilize legal databases (a skill often tested in a very specific, time-sensitive manner).
- Advocacy:Presenting a concise, persuasive argument based on facts and law under timed conditions.
Effective preparation for SQE2 relies on practice, personalized feedback from qualified solicitors, and constant review of the SRA’s detailed marking rubrics to understand exactly how competence is measured.
The QLTS School Legacy: Building Confidence for the Modern Era
The transition from QLTS to SQE is evolutionary, not revolutionary, in terms of the core competencies required by the SRA. A provider with a strong foundation in the QLTS framework is best equipped to guide candidates through the new environment. Their experience in preparing international lawyers for the rigorous demands of the old system translates directly to understanding the depth, breadth, and professional focus required by the SQE. It’s a legacy built on ensuring professional equivalence and competence, which remains the central pillar of the SRA’s new qualification pathway. Leveraging this proven expertise is arguably the single most strategic decision an aspiring solicitor can make.
Securing Your Future: From Candidate to Qualified Solicitor
The path to qualification is demanding, but the standardization offered by the SQE creates a clear, transparent goal. It levels the playing field, making the title of “Solicitor of England and Wales” accessible to the most committed and competent candidates, regardless of their academic background or country of origin. Successful preparation is about more than just passing an exam; it’s about transforming a candidate into a competent, practice-ready legal professional, equipped not just with knowledge, but with the confidence and skills to thrive in the competitive world of law. The future of your legal career is built on the strength of your preparation today.